Mathematics and Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, encompassing its structure, use, and evolution. Mathematics provides valuable tools.
published : 04 April 2024
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, encompassing its structure, use, and evolution. Mathematics provides valuable tools and methods for analyzing and modeling various aspects of language, from phonetics and phonology to syntax, semantics, and pragmatics.
Computational Linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field that applies mathematical and computational techniques to the study of natural language. Mathematical models such as finite state automata, context-free grammars, and hidden Markov models are used to represent and analyze the structure and behavior of language.
By applying mathematical techniques such as machine learning, natural language processing, and statistical modeling, computational linguists can develop algorithms and software tools for tasks such as speech recognition, machine translation, text analysis, and information retrieval.
Quantitative Linguistics
Quantitative linguistics is another branch of linguistics that uses mathematical and statistical methods to study linguistic phenomena. Mathematical models such as Zipf's law, Shannon's entropy, and distributional semantics are used to analyze the distribution and structure of linguistic elements such as words, sounds, and meanings.
By applying mathematical techniques such as statistical analysis, information theory, and network theory, quantitative linguists can uncover patterns and regularities in language data, explore linguistic universals and typologies, and test hypotheses about the cognitive and cultural foundations of language.
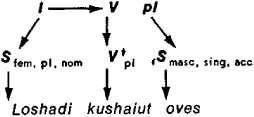
Formal Linguistics
Formal linguistics is a subfield of linguistics that uses mathematical and logical methods to formalize and analyze the structure of natural language. Mathematical models such as formal grammars, logic-based semantics, and automata theory are used to describe and analyze the syntax and semantics of language.
By applying mathematical techniques such as formal logic, set theory, and model theory, formal linguists can develop precise and rigorous descriptions of linguistic structures and rules, explore the computational complexity of linguistic tasks, and investigate the formal properties of human language.
Conclusion
Mathematics plays a vital role in linguistics, providing valuable tools and methods for analyzing and modeling various aspects of language structure, use, and evolution. By applying mathematical techniques such as computational linguistics, quantitative linguistics, and formal linguistics, researchers can gain insights into the underlying principles and mechanisms of human language and develop new approaches for studying and understanding language in all its complexity.
As the fields of mathematics and linguistics continue to intersect and evolve, the role of mathematics in understanding and analyzing language will remain essential in unraveling the mysteries of human communication and cognition.








